



Novel coronavirus (CoV) is a new strain of coronavirus. The disease caused by the novel coronavirus identified first in Wuhan, China, has been given the name – coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). ‘CO’ denotes corona, ‘VI’ for virus, and ‘D’ for disease. The disease was formerly referred to as ‘2019-nCoV’ or ‘2019 novel coronavirus’. The COVID-19 is related to the same family of viruses as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) and some types of common cold.
The virus is transmitted through direct contact with droplets of an infected person (usually via sneezing or coughing), and touching surfaces that are contaminated with the virus. The virus may survive on a surface for several hours.
Since first recorded in China late last year, COVID-19 has spread all over the world, and been declared a pandemic by the WHO.
The worldwide death toll from the novel coronavirus pandemic rose to 259,695 while the total number of infections worldwide is at 3,709,800 on 6th May 2020. Of these cases, at least 1,225,364 are now considered recovered. Many countries are testing only the most serious cases.
In the United States, now the worst-hit country, the death toll is at 71,478 with 1,210,822 infections. United Kingdom is the next most-affected country with 30,150 deaths and 202,355 confirmed infections.
It is followed by Italy with 29,684 deaths and 214,457 confirmed infections and Spain with 25,613 fatalities and 219,329 confirmed infections.
Meanwhile in Asia, the spread continues, China, for the time being, seems to have passed its peak. Globally, most countries have closed offices, schools, and other institutions and many are in complete lockdown.
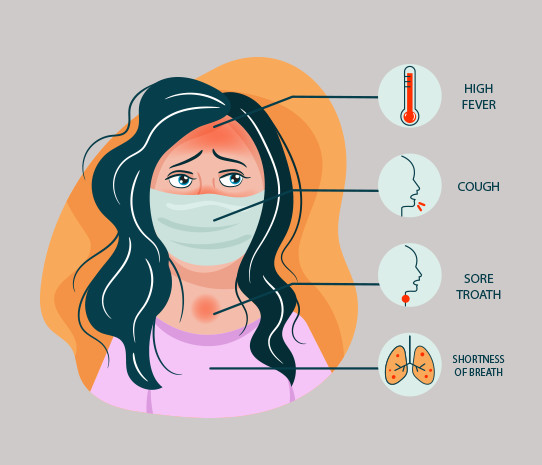
The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, dry cough, and tiredness. Most people recover from the disease without requiring special treatment. The disease can be serious and even fatal for older people, and those with any other long-term medical conditions (such as diabetes, asthma, or heart diseases).
However, the number of asymptomatic patients is also on the rise. At the time of writing, a total of 1,104 asymptomatic cases, including 364 imported from abroad, were under medical observation on the Chinese mainland.
Asymptomatic cases refer to people who are tested positive for the coronavirus but develop no symptoms like fever, dry cough or sore throat. A Chinese official circular said that they are infectious and pose a risk of spreading to others.
Screening of asymptomatic infections must be stepped up, targeting close contacts of confirmed patients, people involved in cluster outbreaks, those exposed to COVID-19, and travelers from areas with high risks of infections.
Our objective is to leverage the synergy between AI and telehealth to institute quick monitoring of remotely collected data anytime, anywhere – saving overall costs while improving care.
RAD365 along with its Healthcare AI initiative – HaiLTH, aims at delivering innovation to support the basic as well as critical healthcare needs of all citizens, throughout any country, irrespective of geographical boundaries, by integrating technology & data and leverage the cloud-based informatics portfolio of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), in combination with –
AI tool built with advanced deep learning methodology and trained using millions of images,
Advanced visualization set-up,
Data analytics,
Panel of on-call radiologists and
Workflow enhancement tools and applications.
HaiLTH’s focus areas of deliverance are as below -
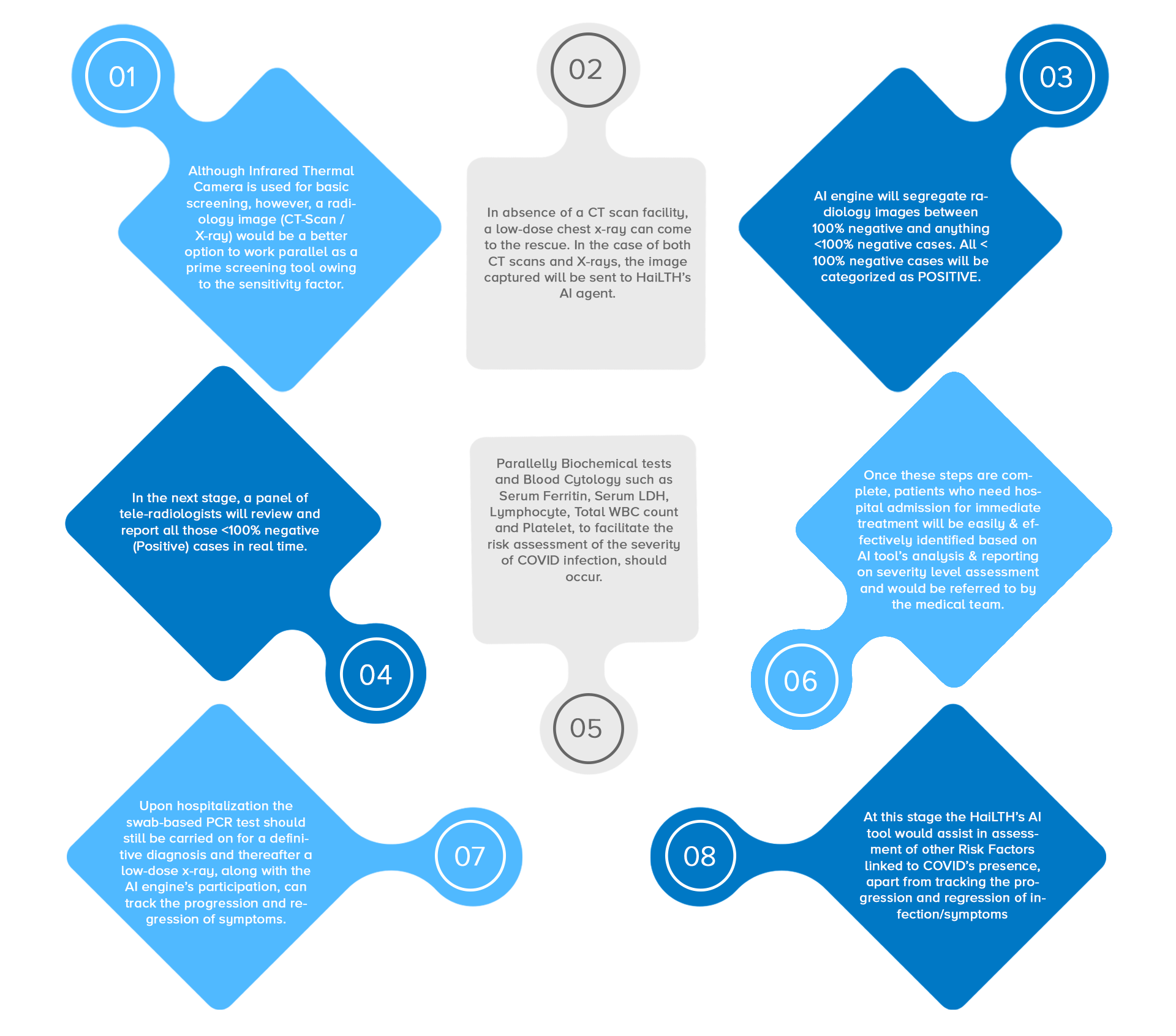
Diagnosing, triaging, and monitoring COVID-19 cases from lung images – both CT Scan and X-ray
Detecting Pneumonia, Lung CA and/or TB-related abnormalities, such as scars, opacities, pleural effusions etc. in the lungs
Real-time detection of abnormalities through our unique AI engine
Identification and classification of cases based on risk levels
Optimization of worklist prioritization for urgent cases
Prediction of other anomalies linked to COVID-19
When it comes to infectious diseases, prevention, surveillance and rapid response play a vital role in slowing or stalling the outbreak. A pandemic such as the current coronavirus outbreak has created a huge challenge for the government and public health officials to gather information instantaneously and coordinate a response. In such a situation, smart screening processes, including those leveraging AI, can play a critical role in detecting an epidemic, building intelligence and knowledge, and augmenting clinical facilities.
Although it may be too late for AI to fully mobilize and help with this pandemic, AI can help humans weather potential pandemics in the future in the following ways:
For most individuals succumbing to COVID-19, the ultimate cause of death has been pneumonia, a condition that causes inflammation and fluid accumulation in our lungs, making it difficult to breathe. Some patients develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a fatal condition whereby the lungs cannot supply enough oxygen to other vital organs of our body.
Pneumonia requires extended hospital stays, and, in some cases, patients are placed in intensive care units (ICU) with mechanical ventilation to help them breathe. As COVID-19 ravages more than 200 countries worldwide, there is a tremendous shortage of mechanical ventilation.
It is, thus, crucial to determine the patients who require more supportive care and those who may recover at home. This is where AI can help analyse lung imaging as part of the clinical research study to diagnose COVID-19 patients and provide a triaging method to shortlist presumptive cases which will definitely need immediate medical care.
HaiLTH’s AI tool does not simply detect patients with pneumonia or those who are possible carriers of SARS-CoV-2 but also facilitates identifying those who are asymptomatic yet are developing pneumonia. Early detection and prevention of pneumonia is crucial to saving lives and reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
The benefits mentioned below will, in return, help maintain and restore economic stability, especially in times of global/national crisis while dealing with an epidemic/pandemic.
Enables radiologists to more effectively and accurately triage COVID-19 cases
Assists healthcare professionals with the early discovery of patients who, if required, can be directly sent to larger hospitals for treatment
Lessens the burden on doctors and healthcare systems with almost instantaneous detection of COVID-19 cases 24x7x365
Empowers the Government Healthcare system with real-time data to strengthen preventive analytics on COVID-19 and other lung-related abnormalities.
Enables facilitating mass-scale screening at nodal points resulting in faster detection
Makes medical care available and easily accessible to a large number of people with varying health conditions
With time, data of COVID-19 patients will be collected, leveraged and built upon by both researchers and data scientists alike to accelerate the development of highly accurate deep learning solutions of HaiLTH to detect future cases and accelerate the treatment of the patients who need it the most.